


Diabetes Technology Revolution: Innovations Transforming Care and Monitoring
Diabetes is a prevalent health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite its widespread occurrence, there are numerous misconceptions surrounding diabetes that often lead to confusion and misinformation. By debunking these myths, we can foster a better understanding of diabetes and promote accurate knowledge about this condition.
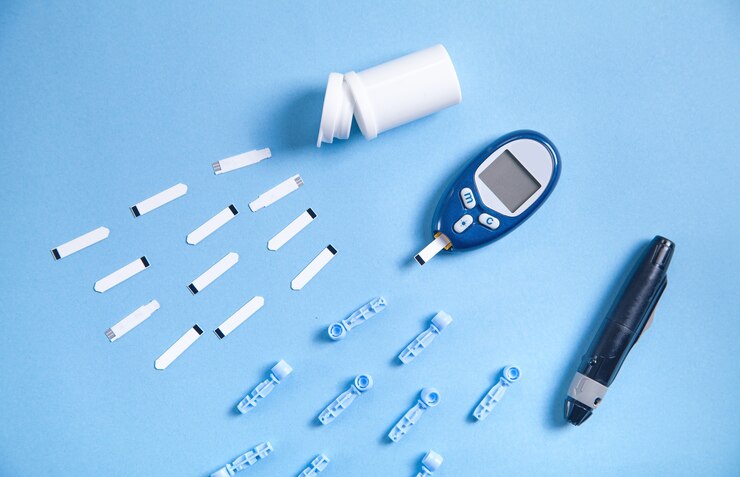
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) systems have emerged as a game-changer in diabetes management. Unlike traditional glucose monitoring methods that require painful finger pricks multiple times a day, CGM systems offer continuous real-time monitoring of glucose levels through a sensor placed under the skin. These sensors transmit glucose readings to a receiver or smartphone, providing users with valuable insights into their glucose trends and helping them make informed decisions about medication, diet, and physical activity.
The integration of CGM technology with insulin pumps has further enhanced diabetes management. Closed-loop systems, also known as artificial pancreas systems, combine CGM data with insulin pump therapy to automatically adjust insulin delivery based on glucose levels. This automation minimizes the risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, offering individuals with diabetes greater peace of mind and improved glycemic control.
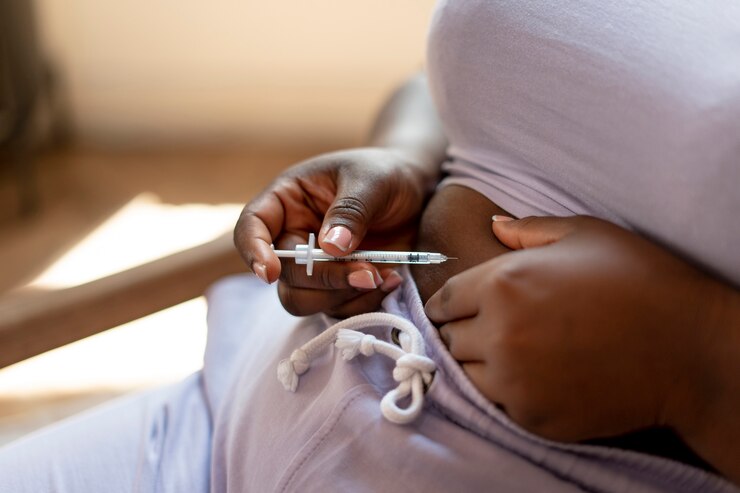
Another notable innovation in diabetes care is the development of smart insulin pens and insulin delivery devices. These devices are equipped with Bluetooth connectivity and companion smartphone apps that enable users to track their insulin doses, set reminders for injections, and analyze their insulin usage patterns over time. Smart insulin pens not only streamline the insulin administration process but also empower individuals to take control of their diabetes management with greater precision and convenience.
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring have emerged as essential tools in diabetes care, particularly in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. Through telehealth platforms, individuals with diabetes can consult healthcare providers, receive education on self-management techniques, and remotely monitor their glucose levels and medication adherence. Remote patient monitoring devices, such as connected glucometers and blood pressure monitors, enable healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health status and intervene promptly when necessary, thereby reducing the need for frequent in-person visits and improving access to care.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are playing an increasingly significant role in diabetes management. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of patient data, including glucose readings, insulin dosages, dietary intake, and physical activity levels, to generate personalized insights and predictive models. By harnessing the power of AI, healthcare providers can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and tailor treatment plans to each individual’s unique needs, ultimately improving outcomes and reducing the burden of diabetes-related complications.
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are also contributing to the diabetes technology revolution. These devices not only track physical activity and monitor vital signs but also integrate with CGM systems to provide users with real-time feedback on their glucose levels and activity levels. By promoting physical activity and encouraging healthy behaviors, wearable devices empower individuals with diabetes to take a proactive approach to their health and well-being.
In conclusion, the diabetes technology revolution is reshaping the landscape of diabetes care and monitoring. From continuous glucose monitoring and closed-loop systems to smart insulin pens and telemedicine, these innovations are empowering individuals with diabetes to manage their condition more effectively and live healthier, more fulfilling lives. As technology continues to evolve, the future holds immense promise for further advancements in diabetes management, ultimately improving outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.