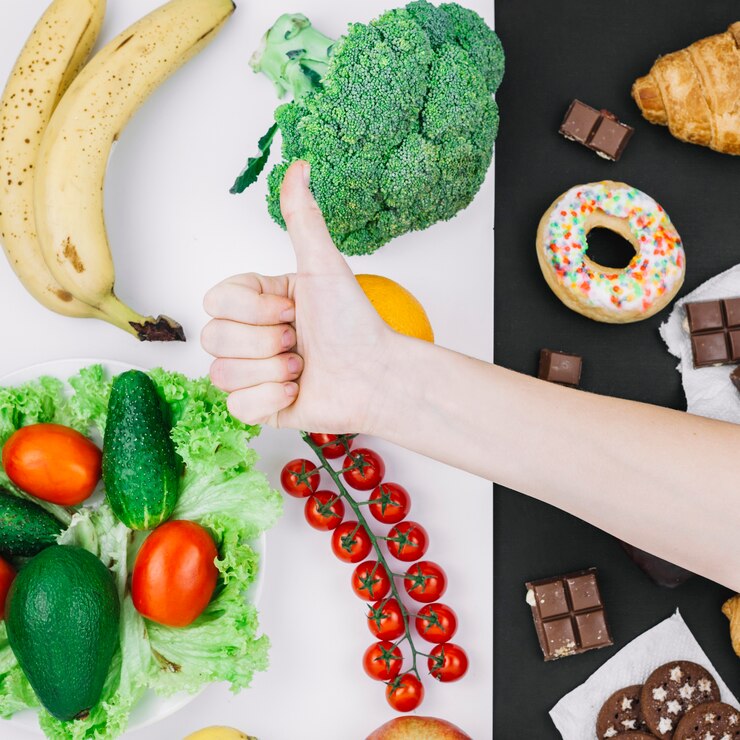



Diabetes and Diet: Crafting a Nutritional Plan for Better Management

Living with diabetes requires careful attention to diet and nutrition. Crafting a tailored nutritional plan can play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels, promoting overall health, and preventing complications. Here, we’ll explore key considerations and tips for creating an effective dietary approach for diabetes management.
Understanding Diabetes:
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, resulting from either insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of insulin by the body. There are primarily two types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood and is characterized by the immune system attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor dietary choices.
The Role of Diet in Diabetes Management:
Diet plays a central role in managing diabetes by influencing blood sugar levels, weight management, and overall health. A well-balanced diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Key Components of a Diabetic-Friendly Diet:
- Carbohydrates: Monitor carbohydrate intake as they have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Focus on complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, which are rich in fiber and digested more slowly, leading to better blood sugar control.
- Proteins: Include lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes in your meals. Protein helps maintain muscle mass, promotes satiety, and stabilizes blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Fats: Choose heart-healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado, nuts, and seeds. These fats can help improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease, a common complication of diabetes.
- Fiber: Aim for adequate fiber intake from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, helps regulate bowel movements, and promotes a feeling of fullness.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. Use smaller plates, measure portions, and pay attention to hunger and satiety cues.
- Meal Timing: Spread out meals evenly throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Avoid skipping meals, and consider incorporating healthy snacks between meals to prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Hydration: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Limit sugary beverages and opt for water, herbal tea, or infused water instead.
Practical Tips for Crafting a Nutritional Plan:
- Consult a Registered Dietitian: Work with a registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes management to develop a personalized meal plan tailored to your individual needs, preferences, and lifestyle.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to understand how different foods affect your body and make adjustments to your diet as needed.
- Stay Consistent: Establish consistent eating patterns and meal timings to help stabilize blood sugar levels and optimize medication effectiveness.
- Be Flexible: While consistency is essential, allow for flexibility in your diet to accommodate social events, special occasions, and cravings. Focus on making healthy choices most of the time rather than striving for perfection.
- Educate Yourself: Take the time to learn about nutrition labels, portion sizes, and how various foods impact blood sugar levels. Knowledge is empowering and enables you to make informed decisions about your diet.
In conclusion, managing diabetes through diet requires a holistic approach that emphasizes balanced nutrition, portion control, and lifestyle modifications. By working closely with healthcare professionals and adopting healthy eating habits, individuals with diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall quality of life.


